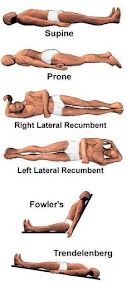
ANATOMICAL POSITION: -
It is defined as standing up straight and facing forward with the arms to the side and the palms facing forward. The feet are PARALLEL slightly apart and the toes point forward. AS SHOWEN IN
BELOW IMAGE -
-. Prone describes a face-down orientation, and
- supine describes a face up orientation. These terms are sometimes used in describing the position of the body during specific,
physical examinations.
Regions of the Human Body
• Anterior (or ventral) describes the front or direction toward the front of the body. The toes are anterior to the
foot.
• Posterior (or dorsal) describes the back or direction toward the back of the body. The popliteus is posterior to the
patella.
• Superior (or cranial) describes a position above or higher than another part of the body proper. The orbits are
superior to the oris.
• Inferior (or caudal) describes a position below or lower than another part of the body proper; near or toward the
tail (in humans, the coccyx, or lowest part of the spinal column). The pelvis is inferior to the abdomen.
• Lateral describes the side or direction toward the side of the body. The thumb (pollex) is lateral to the digits.
• Medial describes the middle or direction toward the middle of the body. The hallux is the medial toe.
• Proximal describes a position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body. The
brachium is proximal to the antebrachium.
• Distal describes a position in a limb that is farther from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body. The crus
is distal to the femur.
• Superficial describes a position closer to the surface of the body. The skin is superficial to the bones.
• Deep describes a position farther from the surface of the body. The brain is deep to the skull.
Directional Terms Applied to the Human Body:
• The sagittal plane divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides. If this vertical plane runs
directly down the middle of the body, it is called the midsagittal or median plane. If it divides the body into unequal
right and left sides, it is called a parasagittal plane or less commonly a longitudinal section.
• The frontal plane divides the body or an organ into an anterior (front) portion and a posterior (rear) portion. The
frontal plane is often referred to as a coronal plane. (“Corona” is Latin for “crown.”)
• The transverse (or horizontal) plane divides the body or organ horizontally into upper and lower portions.
Transverse planes produce images referred to as cross sections.
Regions and Quadrants of the Peritoneal Cavity
A. nine abdominal regions
B. four abdominal
quadrants in the peritoneal cavity
Opposition of thumb
Abduction of fingers
Internal rotation of arm
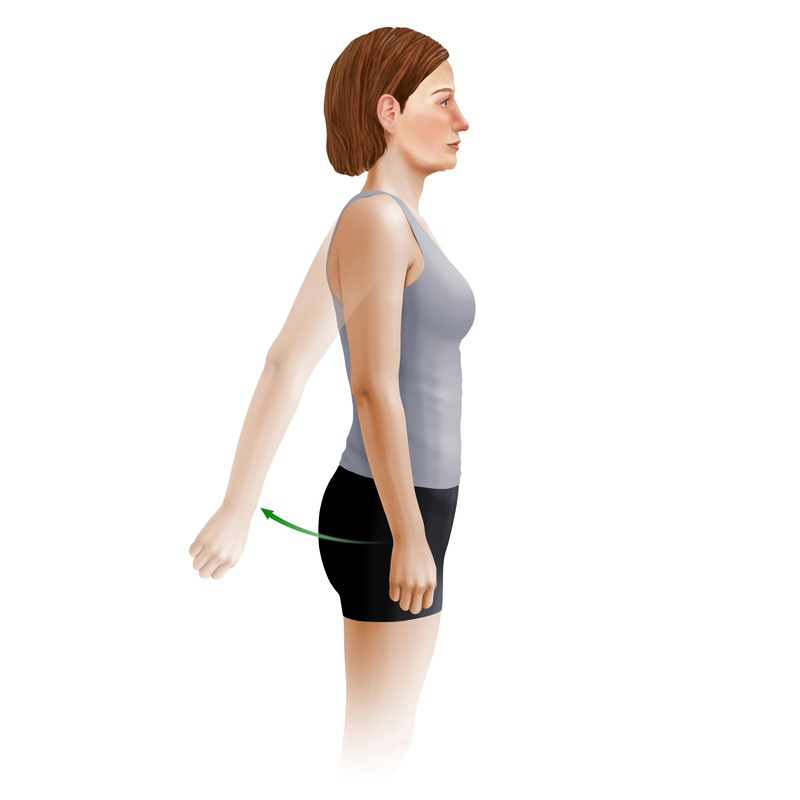
Adduction of arm
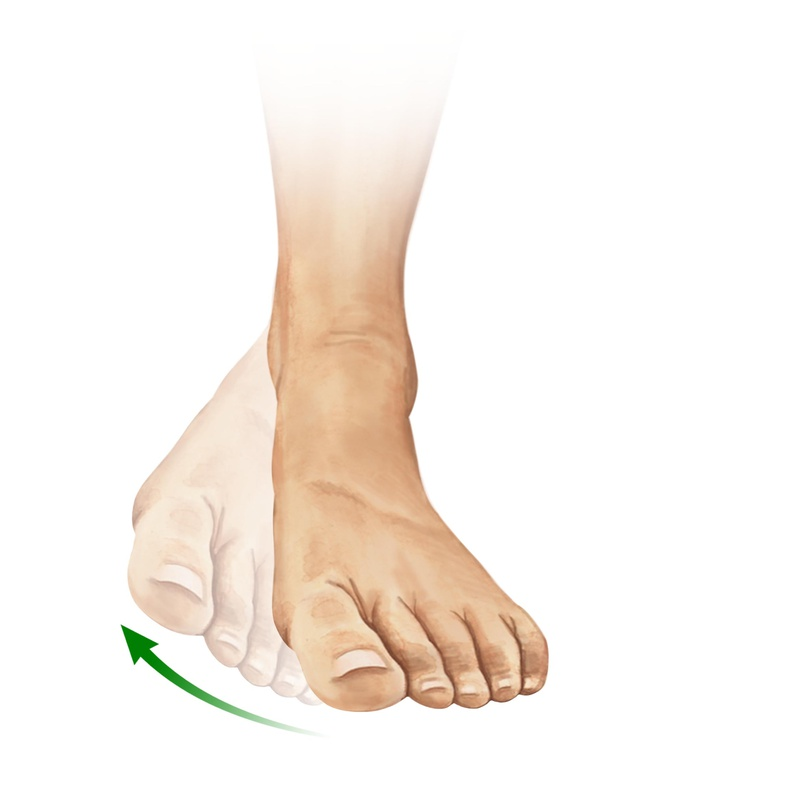
Plantar flexion of foot