⚕️ BRIGHTING MEDICO SACHIN
medical e-learning, anatomical description of human body, tissue histology, next exam update, fmge last year asked questions
Monday, 14 August 2023
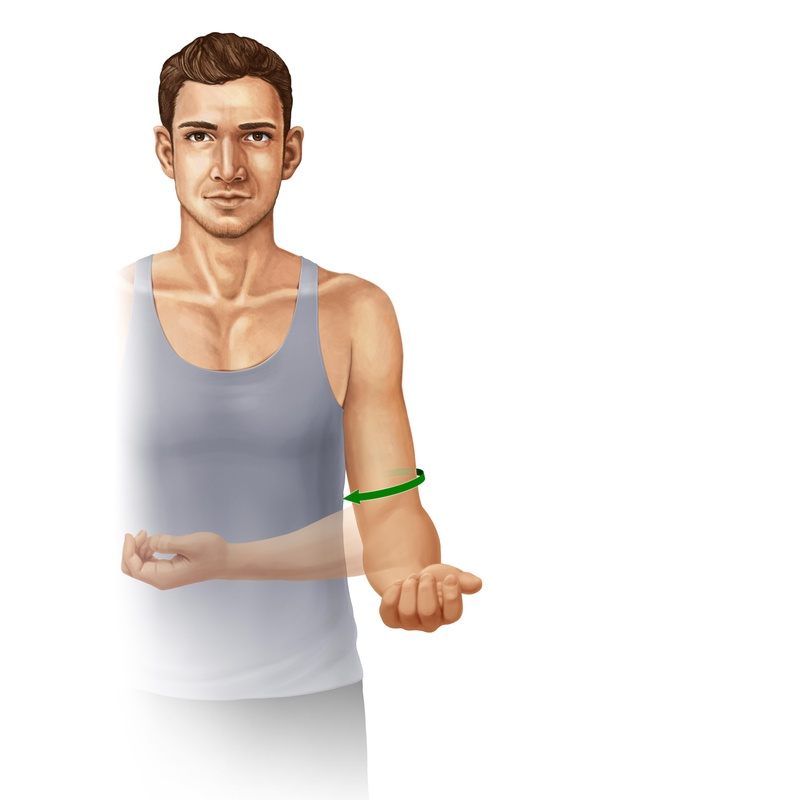
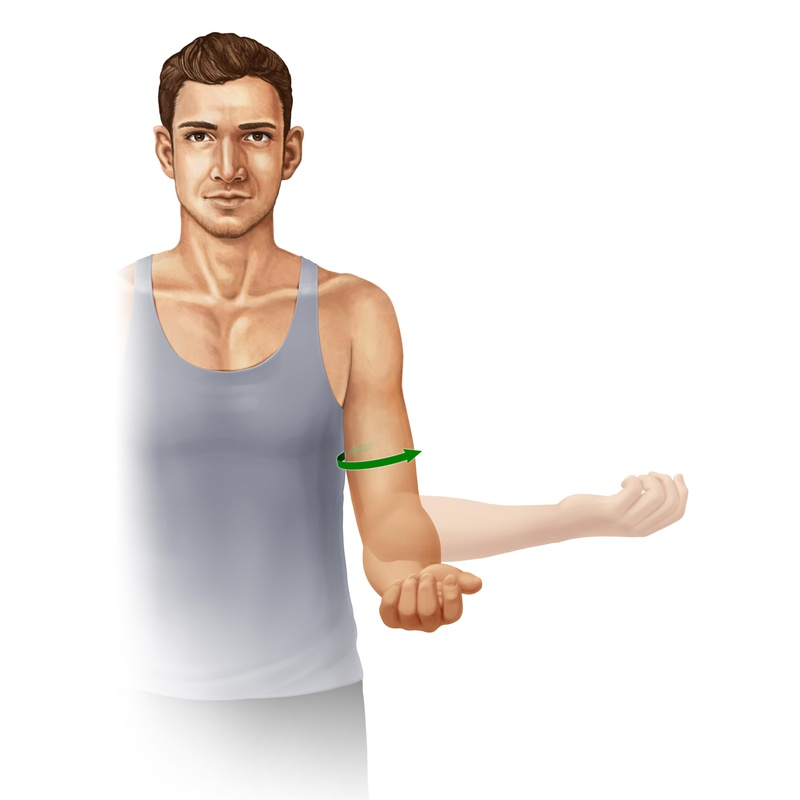
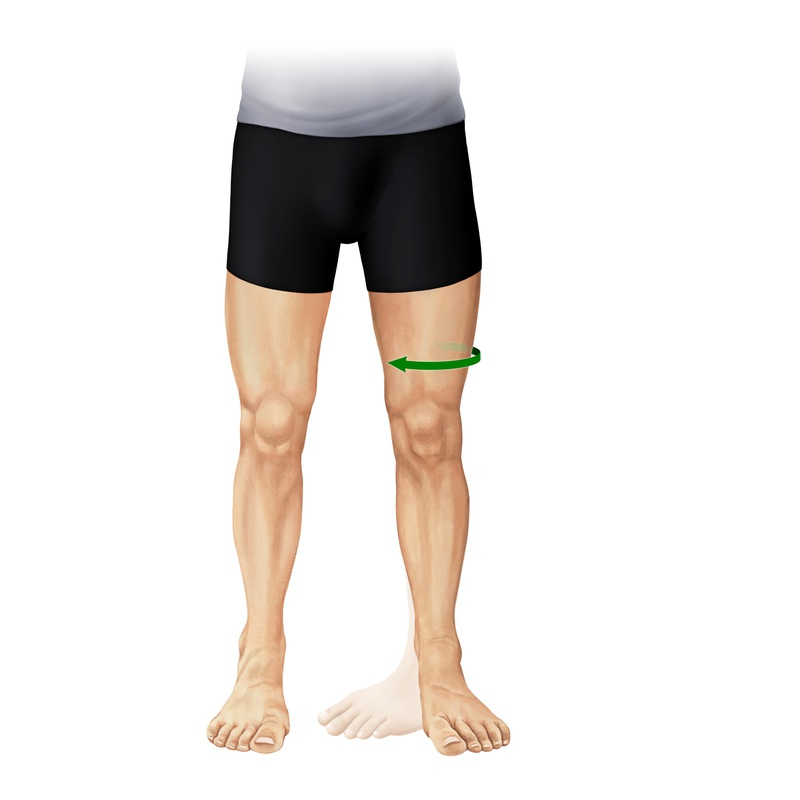
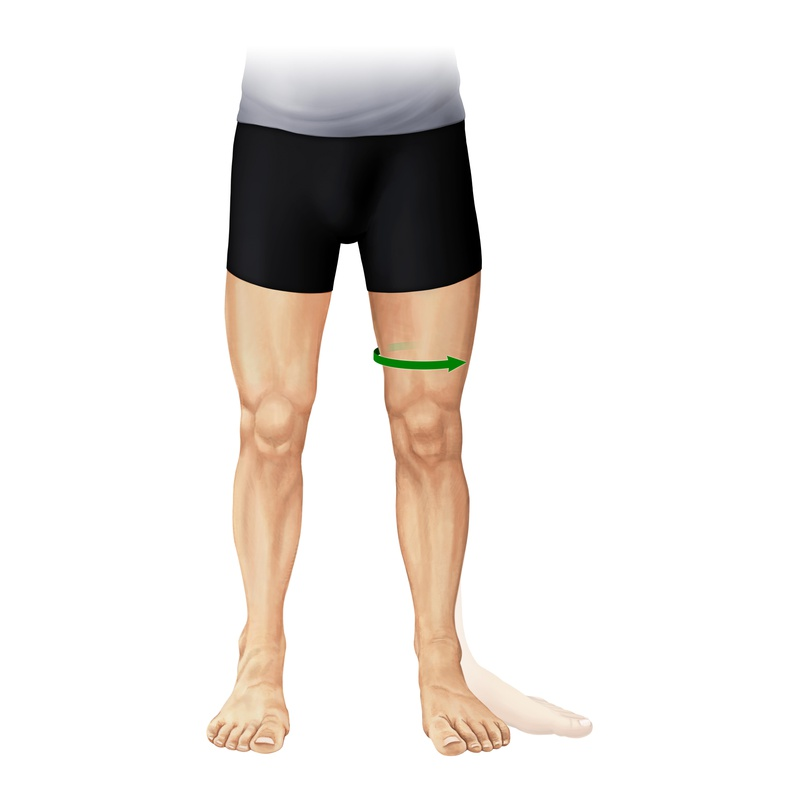
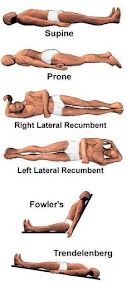
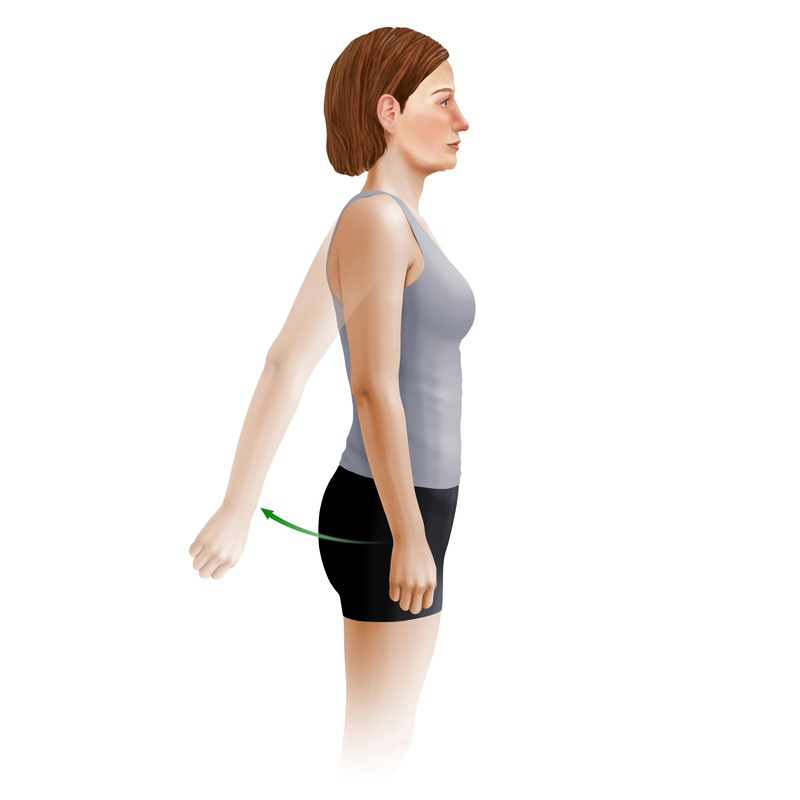
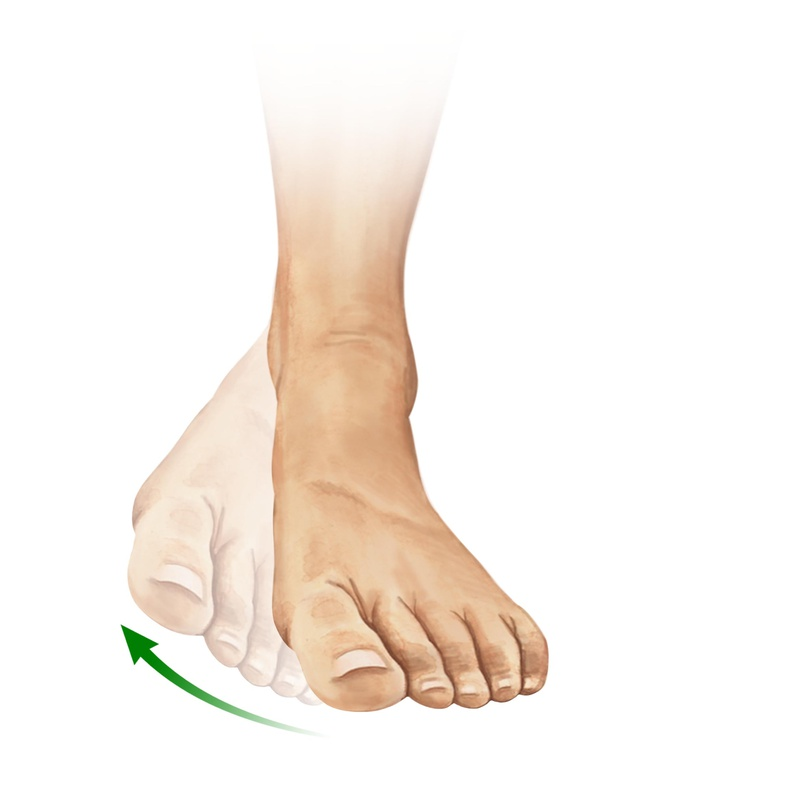
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY AND POSITIONS
Friday, 28 July 2023
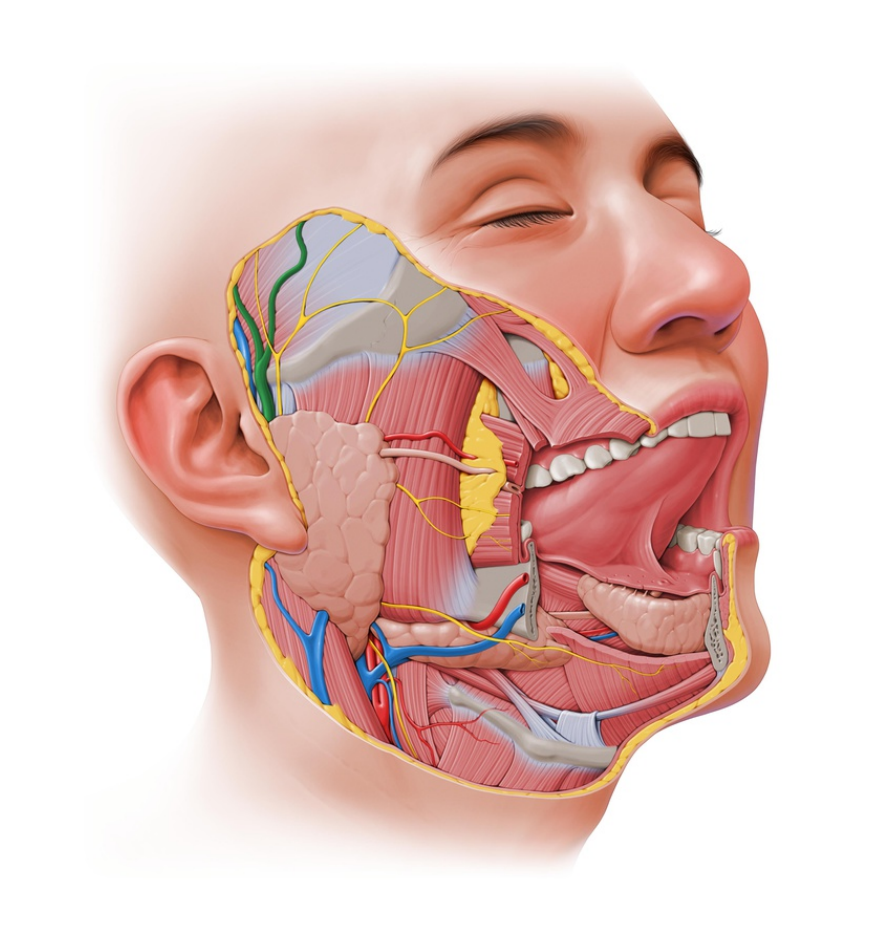
ANATOMY HEAD FLASH CARDS
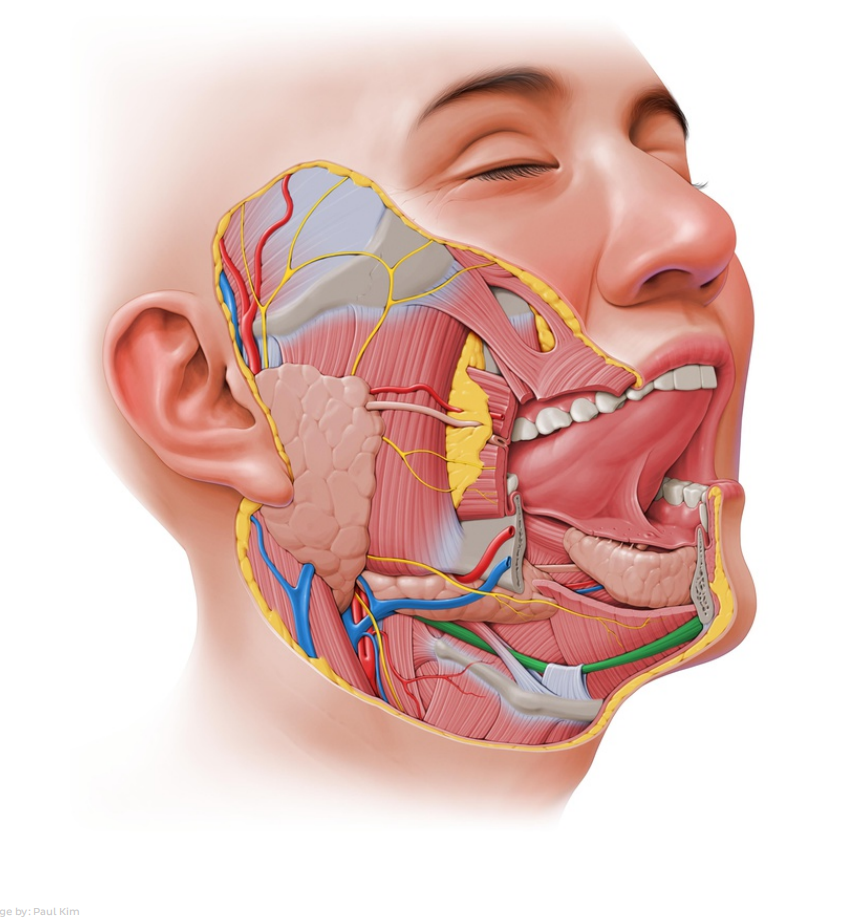
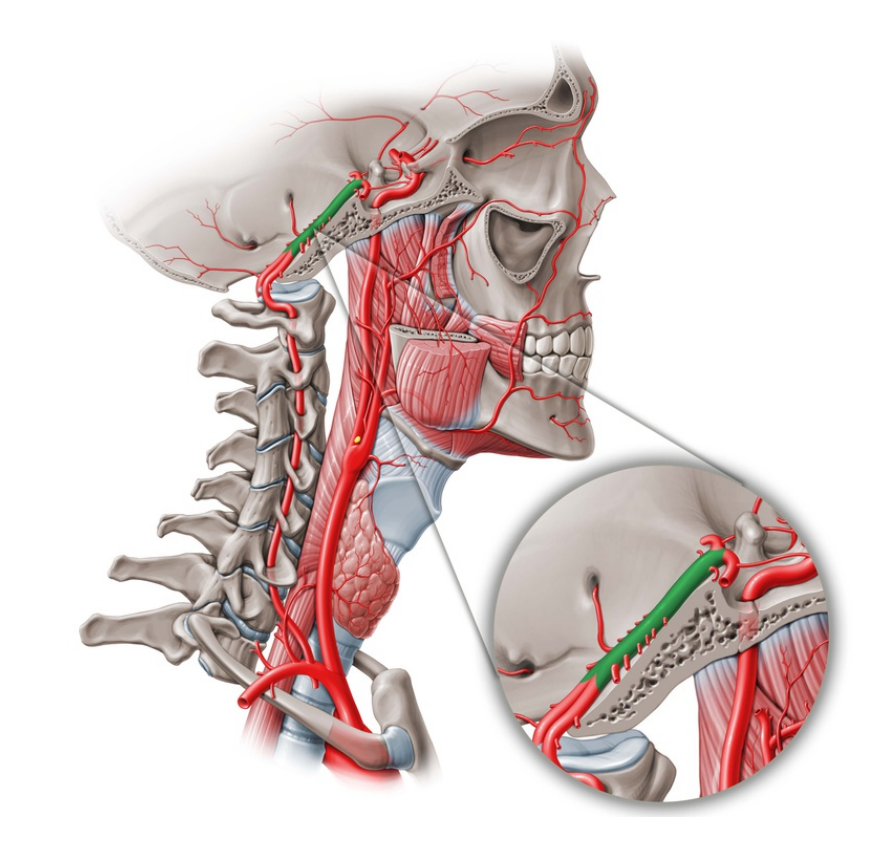
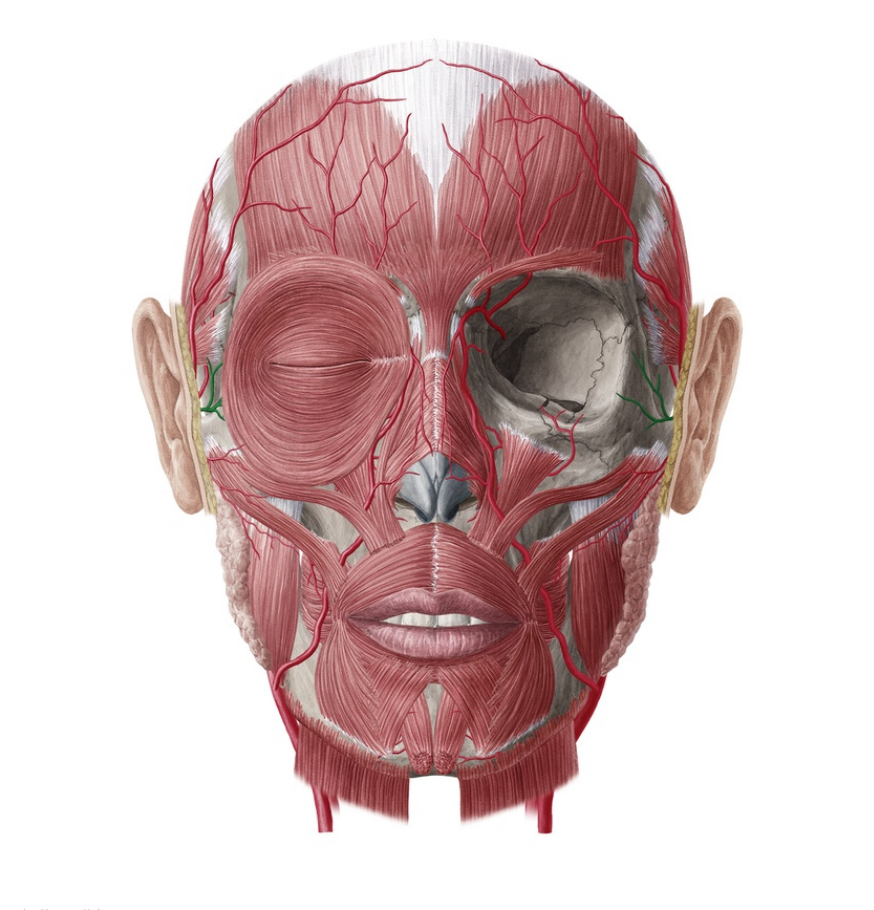
HELLO EVERYONE, I AM SHARING WITH YOU ANATOMY FLASHCARDS WITH SHORT EXPLANATION, SWEET AND CLEAR IMAGE OF THE HEAD (MUSCLES, BONES, AND NERVES BRIEFLY)
QUESTION
What structure is shown here?
-Levator labii superioris
LATIN Musculus levator labii superioris
QUESTION
What structure is shown here?
-Supratrochlear vein
LATIN Vena supratrochlearis
-Middle temporal vein
LATIN Vena temporalis media
-Cervical branch of facial nerve
LATIN Ramus colli nervi facialis
-Lateral pterygoid muscle
LATIN
Musculus pterygoideus
lateralis
ENGLISH- Digastric muscle
LATIN- Musculus digastricus
ORIGINS- Digastric fossa, Mastoid notch
INSERTIONS- Body of hyoid
INNERVATIONS- Facial nerve, Mandibular nerve
FUNCTIONS -Elevates the body of hyoid.
-Basilar artery
LATIN Arteria basilaris
-External carotid artery
LATIN Arteria carotis externa
-Greater occipital nerve
LATIN Nervus occipitalis major
ENGLISH - Superficial part of medial pterygoid muscle
LATIN - Pars superficialis musculi pterygoidei medialis
ORIGINS- Maxillary tuberosity
INSERTIONS- Pterygoid tuberosity
INNERVATIONS- Mandibular nerve
FUNCTIONS- Elevates the mandible.
-Posterior auricular vein
LATIN Vena auricularis posterior
LATIN
Musculus levator labii
superioris alaeque nasi
-Zygomaticoorbital artery
LATIN Arteria zygomaticoorbitalis
LATIN
Arteria occipitalis
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY AND POSITIONS
ANATOMICAL POSITION: - It is defined as standing up straight and facing forward with the arms to the side and the palms facing forwar...

-
HELLO EVERYONE, I AM SHARING WITH YOU ANATOMY FLASHCARDS WITH SHORT EXPLANATION, SWEET AND CLEAR IMAGE OF THE HEAD (MUSCLES, BONES, AND ...
-
FMGE June 2022 Micro Q1. Which among the following methods is used to sterilize a glass petri dish? 1.Autoclaving at 121 degree celsius fo...
-
EPITHELIAL TISSUE There are 4 basic types of tissue:- 1.connective tissue 2. epithelial tissue 3. muscle tissue 4.nervous ti...